
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a cornerstone for innovation, scalability, and efficiency. Among the leading providers in this domain is Oracle Corporation, renowned for its enterprise software solutions. Oracle Cloud represents the company’s foray into delivering comprehensive cloud services, catering to a myriad of business needs. This article delves deep into Oracle Cloud’s offerings, architecture, benefits, and its positioning in the competitive cloud market.
1. Evolution of Oracle Cloud
Oracle’s journey into cloud computing began with the realization that enterprises required more than just on-premises solutions. Recognizing the shift towards cloud-based infrastructures, Oracle introduced its cloud services to offer scalable, secure, and efficient solutions.
Key Milestones:
- 2016: Launch of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), marking Oracle’s significant entry into the cloud market.
- 2018: Introduction of Generation 2 Cloud, emphasizing security and performance.
- 2020: Partnership with Zoom, showcasing Oracle Cloud’s capability to handle massive workloads.
- 2023: Expansion to over 44 cloud regions globally, emphasizing Oracle’s commitment to global accessibility.

2. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI): The Backbone
At the heart of Oracle’s cloud services lies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), designed to support both traditional and modern workloads with high performance and reliability.
Key Features:
- Compute Services: Offers virtual machines, bare metal servers, and container orchestration for diverse workloads.
- Storage Solutions: Provides block, object, file, and archive storage options to cater to various data needs.
- Networking: Features Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs), load balancers, and FastConnect for secure and efficient connectivity.
- Security: Implements a security-first architecture with features like identity and access management, encryption, and threat detection.
3. Comprehensive Service Offerings
Oracle Cloud delivers a broad spectrum of services across different models:
a. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
- Compute: Flexible compute options, including virtual machines and bare metal instances.
- Storage: Scalable storage solutions for diverse data requirements.
- Networking: Advanced networking features ensuring secure and efficient data transfer.
b. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
- Databases: Autonomous Database, MySQL, and NoSQL services.
- Analytics: Tools for data visualization, machine learning, and big data processing.
- Integration: Services facilitating seamless integration between applications and data sources.
c. Software as a Service (SaaS):
- Enterprise Applications: Solutions for ERP, HCM, SCM, and CX, enabling businesses to streamline operations.

4. Oracle Autonomous Database: Revolutionizing Data Management
One of Oracle’s standout innovations is the Autonomous Database, a self-driving, self-securing, and self-repairing database system.
Benefits:
- Automation: Eliminates manual database management tasks.
- Security: Automatically applies security patches and updates.
- Performance: Continuously optimizes performance based on workload patterns.

5. Global Infrastructure and Data Centers
Oracle Cloud’s global footprint ensures that businesses can deploy applications closer to their users, enhancing performance and compliance.
Highlights:
- 44+ Cloud Regions: Spanning across North America, Europe, Asia, and other regions.
- Dedicated Regions: Offers cloud services within customer data centers for specific compliance and latency requirements.
- Sovereign Clouds: Tailored for government and regulated industries with stringent data residency needs.

6. Security and Compliance: A Core Tenet
Oracle Cloud places a strong emphasis on security, ensuring that customer data remains protected.
Security Measures:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user access and permissions.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted both at rest and in transit.
- Compliance Certifications: Meets global standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
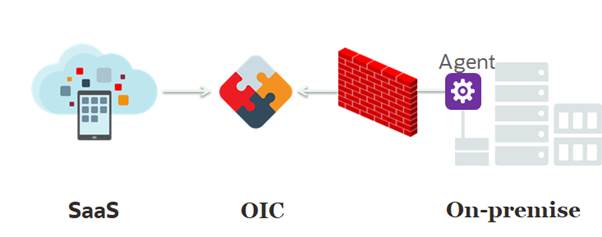
7. Integration and Interoperability
Understanding the diverse IT landscapes of enterprises, Oracle Cloud offers robust integration capabilities.
Features:
- Oracle Integration Cloud: Connects applications and automates business processes.
- APIs and Connectors: Facilitates integration with third-party applications and services.
- Hybrid Cloud Support: Enables seamless operation between on-premises and cloud environments.
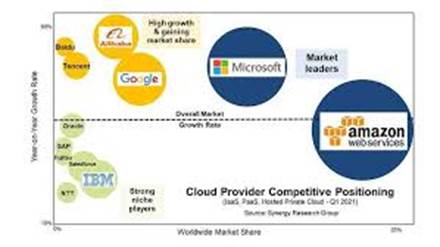
8. Competitive Positioning in the Cloud Market
While AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the cloud market, Oracle Cloud has carved a niche for itself, especially among enterprises reliant on Oracle applications.
Strengths:
- Enterprise Focus: Deep integration with Oracle’s suite of enterprise applications.
- Performance: High-performance computing capabilities suitable for demanding workloads.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Competitive pricing models, especially for existing Oracle customers.
Image Source: Oracle
9. Real-World Use Cases
Several organizations have leveraged Oracle Cloud to transform their operations:
- Zoom: Migrated to Oracle Cloud to handle increased demand during the pandemic.
- Mitsubishi Electric: Utilized Oracle Cloud for data consolidation and analytics.
- Mazda: Adopted Oracle’s Autonomous Database for manufacturing data management.

10. Future Outlook
Oracle continues to invest in expanding its cloud capabilities:
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing services to support AI-driven applications.
- Edge Computing: Developing solutions for low-latency applications.
- Sustainability: Committed to powering data centers with 100% renewable energy by 2025.
Conclusion
Oracle Cloud stands as a robust and comprehensive cloud platform, tailored for enterprises seeking performance, security, and integration capabilities. With its continuous innovations and commitment to customer success, Oracle Cloud is poised to play a pivotal role in the future of enterprise computing.
Note: All images are sourced from Oracle’s official website and are used here for illustrative purposes.